1
What is one advantage of using the cut-through switching method instead of the store-and-forward switching method?
has a positive impact on bandwidth by dropping most of the invalid frames
makes a fast forwarding decision based on the source MAC address of the frame
has a lower latency appropriate for high-performance computing applications*
provides the flexibility to support any mix of Ethernet speeds
2
A network designer must provide a rationale to a customer for a design which will move an enterprise from a flat network topology to a hierarchical network topology. Which two features of the hierarchical design make it the better choice? (Choose two.)
reduced cost for equipment and user training
less required equipment to provide the same performance levels
simpler deployment for additional switch equipment*
easier to provide redundant links to ensure higher availability*
lower bandwidth requirements
3
What are two advantages of modular switches over fixed-configuration switches? (Choose two.)
availability of multiple ports for bandwidth aggregation
lower forwarding rates
need for fewer power outlets*
lower cost per switch
increased scalability*
4
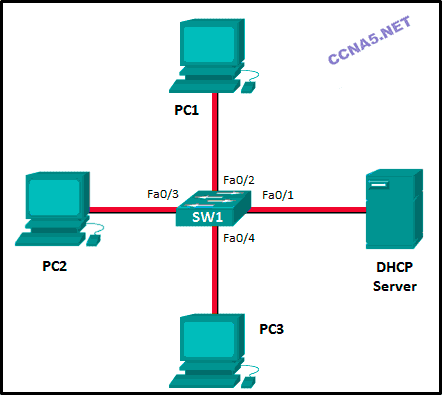
Refer to the exhibit. Consider that the main power has just been restored. PC1 asks the DHCP server for IPv4 addressing. The DHCP server sends it an IPv4 address. While PC2 is still booting up, PC3 issues a broadcast IPv4 DHCP request. To which port will SW1 forward this request?
to Fa0/1, Fa0/2, and Fa0/4 only
to Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, and Fa0/4
to Fa0/1 and Fa0/2 only
to Fa0/1, Fa0/2, and Fa0/3 only*
to Fa0/1 only
5
What is one function of a Layer 2 switch?
forwards data based on logical addressing
learns the port assigned to a host by examining the destination MAC address
duplicates the electrical signal of each frame to every port
determines which interface is used to forward a frame based on the destination MAC address*
6
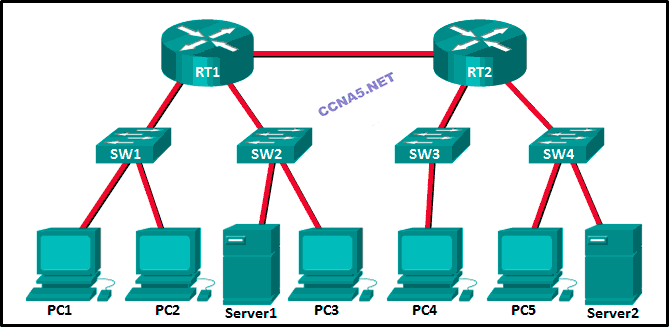
Refer to the exhibit. Fill in the blank.
There are ” 12 ” collision domains in the topology.
7
What is a collapsed core in a network design?
a combination of the functionality of the access, distribution, and core layers
a combination of the functionality of the access and core layers
a combination of the functionality of the distribution and core layers*
a combination of the functionality of the access and distribution layers
8
What are two reasons a network administrator would segment a network with a Layer 2 switch? (Choose two.)
to enhance user bandwidth*
to eliminate virtual circuits
to create more broadcast domains
to isolate traffic between segments*
to isolate ARP request messages from the rest of the network
to create fewer collision domains
9

Refer to the exhibit.
How is a frame sent from PCA forwarded to PCC if the MAC address table on switch SW1 is empty?
SW1 forwards the frame directly to SW2. SW2 floods the frame to all ports connected to SW2, excluding the port through which the frame entered the switch.
SW1 floods the frame on all ports on the switch, excluding the interconnected port to switch SW2 and the port through which the frame entered the switch.
SW1 floods the frame on all ports on SW1, excluding the port through which the frame entered the switch.*
SW1 drops the frame because it does not know the destination MAC address.
10 Match the forwarding characterictic to its type.(Not all options are used.)
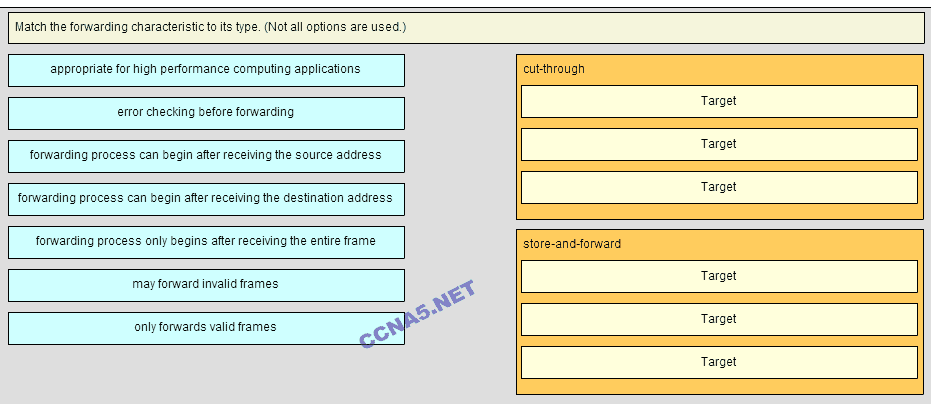
Place the options in the following order:
cut-throught:
+appropriate for high perfomance computing applications
+forwarding process can be begin after receiving the destination address
+may forward invalid frames
store-and-forward:
#error checking before forwarding
#forwarding process only begins after receiving the entire frame
#only forwards valid frames
11
What is a basic function of the Cisco Borderless Architecture distribution layer?
aggregating Layer 3 routing boundaries*
aggregating all the campus blocks
acting as a backbone
providing access to the user
12
ABC, Inc. has about fifty hosts in one LAN. The administrator would like to increase the throughput of that LAN. Which device will increase the number of collision domains and thereby increase the throughput of the LAN?
hub
host
NIC
switch*
13
What does the term “port density” represent for an Ethernet switch?
the numbers of hosts that are connected to each switch port
the speed of each port
the memory space that is allocated to each switch port
the number of available ports*
14
Which type of transmission does a switch use when the destination MAC address is not contained in the MAC address table?
anycast
unicast
broadcast*
multicast
15
What is a basic function of the Cisco Borderless Architecture access layer?
aggregates Layer 3 routing boundaries
provides high availability
aggregates Layer 2 broadcast domains
provides access to the user*
16
What information is added to the switch table from incoming frames?
source MAC address and incoming port number*
destination MAC address and incoming port number
destination IP address and incoming port number
source IP address and incoming port number
17
Fill in the blank.
A “converged” network is one that uses the same infrastructure to carry voice, data, and video signals.
18
An administrator purchases new Cisco switches that have a feature called StackPower. What is the purpose of this feature?
It enables many switches to be connected with a special fiber-optic power cable to provide higher bandwidth.
It enables the sharing of power among multiple stackable switches.*
It enables many switches to be connected to increase port density.
It enables many switches to be physically stacked in an equipment rack.
It enables AC power for a switch to be provided from a powered patch panel.
19
Which switch form factor should be used when large port density, fault tolerance, and low price are important factors?
fixed-configuration switch
modular switch
stackable switch*
rackable 1U switch
20

Refer to the exhibit. Fill in the blank.
There are ” 5 ” broadcast domains in the topology.
21 What tool is important to consider for use when making hardware improvement decisions about switches?
switched virtual interfaces
authentication servers
multilayer switching
traffic flow analysis*
22 What is the maximum wire speed of a single port on a 48-port gigabit switch?
1000 Mb/s*
48 Mb/s
48 Gb/s
100 Mb/s
23 When the installation of a network infrastructure is being planned, which technology will allow power to be provided via Ethernet cabling to a downstream switch and its connected devices?
PoE pass-through*
Gigabit Ethernet
wireless APs and VoIP phones
PoE
24 Match the function to the corresponding switch type. (Not all options are used.)
Layer 2 switches
[+] typically used in the access layer of a switched network
[+] forward traffic based on information in the Ethernet header
Multilayer switches
[#] can build a routing table
[#] supports a few routing protocols
25. A local law firm is redesigning the company network so that all 20 employees can be connected to a LAN and to the Internet. The law firm would prefer a low cost and easy solution for the project. What type of switch should be selected?
StackWise
StackPower
modular configuration
fixed configuration*
stackable configuration
26. What is a definition of a two-tier LAN network design?
access, distribution, and core layers collapsed into one tier, with a separate backbone layer
distribution and core layers collapsed into one tier, and the access layer on a separate tier*
access and distribution layers collapsed into one tier, and the core layer on a separate tier
access and core layers collapsed into one tier, and the distribution layer on a separate tier
27. What two criteria are used by a Cisco LAN switch to decide how to forward Ethernet frames? (Choose two.)
path cost
destination MAC address*
egress port
ingress port*
destination IP address
28. Which statement describes the microsegmentation feature of a LAN switch?
The switch will not forward broadcast frames.
All ports inside the switch form one collision domain.
Frame collisions are forwarded.
Each port forms a collision domain.*
29. Which two previously independent technologies should a network administrator attempt to combine after choosing to upgrade to a converged network infrastructure? (Choose two.)
mobile cell phone traffic
scanners and printers
electrical system
analog and VoIP phone traffic*
user data traffic*
30. What is the destination address in the header of a broadcast frame?
FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF*
0.0.0.0
11-11-11-11-11-11
255.255.255.255
31. Which type of address does a switch use to build the MAC address table?
destination IP address
source IP address
destination MAC address
source MAC address*
32. Which two previously independent technologies should a network administrator attempt to combine after choosing to upgrade to a converged network infrastructure? (Choose two.)
mobile cell phone traffic
scanners and printers
electrical system
analog and VoIP phone traffic*
user data traffic*
33.

Refer to the exhibit. How many broadcast domains are displayed?
4
16
8*
1
55
34.

Refer to the exhibit. Fill in the blank.
How many collision domains are shown in the topology? __2__
35.

Place the options in the following order:
Access layer
[+] represents the network edge
[+] provides network access to the user
Distribution layer
[#] implements network access policy
[#] establishes Layer 3 routing boundaries
Core layer
[*] provides high-speed backbone connectivity
[*] functions as an aggregator for all the campus blocks
36.

Match the borderless switched network guidline description to the principle (not all options used)
Place the options in the following order:
allows intelligent traffic load sharing by using all network resources -> flexibility
facilitates understanding the role of each device at every tier, simplifies deployment, operation, management, and reduces fault domains at every tier -> hierarchical
allows seamless network expansion and integrated service enablement on an on-demand basis -> modularity
satisfies user expectations for keeping the network always on -> resiliency
37. Which network device can be used to eliminate collisions on an Ethernet network?
hub
firewall
router
switch*
38.

Refer to the exhibit. Consider that the main power has just been restored. PC3 issues a broadcast IPv4 DHCP request. To which port will SW1 forward this request?
to Fa0/1, Fa0/2, and Fa0/3 only*
to Fa0/1 and Fa0/2 only
to Fa0/1 only
to Fa0/1, Fa0/2, and Fa0/4 only
to Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, and Fa0/4
1. What are two advantages of static routing over dynamic routing? (Choose two.)
Static routing is more secure because it does not advertise over the network.*
Static routing scales well with expanding networks.
Static routing requires very little knowledge of the network for correct implementation.
Static routing uses fewer router resources than dynamic routing.*
Static routing is relatively easy to configure for large networks.
2. Refer to the exhibit. What routing solution will allow both PC A and PC B to access the Internet with the minimum amount of router CPU and network bandwidth utilization?

Configure a static route from R1 to Edge and a dynamic route from Edge to R1.
Configure a static default route from R1 to Edge, a default route from Edge to the Internet, and a static route from Edge to R1.*
Configure a dynamic route from R1 to Edge and a static route from Edge to R1.
Configure a dynamic routing protocol between R1 and Edge and advertise all routes.
3. What is the correct syntax of a floating static route?
ip route 209.165.200.228 255.255.255.248 serial 0/0/0
ip route 209.165.200.228 255.255.255.248 10.0.0.1 120*
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 serial 0/0/0
ip route 172.16.0.0 255.248.0.0 10.0.0.1
4. What is a characteristic of a static route that matches all packets?
It backs up a route already discovered by a dynamic routing protocol.
It uses a single network address to send multiple static routes to one destination address.
It identifies the gateway IP address to which the router sends all IP packets for which it does not have a learned or static route.*
It is configured with a higher administrative distance than the original dynamic routing protocol has.
5. What type of route allows a router to forward packets even though its routing table contains no specific route to the destination network?
dynamic route
default route*
destination route
generic route
6. Why would a floating static route be configured with an administrative distance that is higher than the administrative distance of a dynamic routing protocol that is running on the same router?
to be used as a backup route*
to load-balance the traffic
to act as a gateway of last resort
to be the priority route in the routing table
7. A company has several networks with the following IP address requirements:
IP phones – 50
PCs – 70
IP cameras – 10
wireless access points – 10
network printers – 10
network scanners – 2
Which block of addresses would be the minimum to accommodate all of these devices if each type of device was on its own network?
172.16.0.0/25
172.16.0.0/24*
172.16.0.0/23
172.16.0.0/22
8. What happens to a static route entry in a routing table when the outgoing interface associated with that route goes into the down state?
The static route is removed from the routing table.*
The router polls neighbors for a replacement route.
The static route remains in the table because it was defined as static.
The router automatically redirects the static route to use another interface.
9. The network administrator configures the router with the ip route 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.2.2 command. How will this route appear in the routing table?
C 172.16.1.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0
S 172.16.1.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0
C 172.16.1.0 [1/0] via 172.16.2.2
S 172.16.1.0 [1/0] via 172.16.2.2*
10. Refer to the exhibit. What two commands will change the next-hop address for the 10.0.0.0/8 network from 172.16.40.2 to 192.168.1.2? (Choose two.)

A(config)# no network 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 172.16.40.2
A(config)# no ip address 10.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 172.16.40.2
A(config)# no ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 172.16.40.2*
A(config)# ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 s0/0/0
A(config)# ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 192.168.1.2*
11. Which type of static route that is configured on a router uses only the exit interface?
recursive static route
directly connected static route*
fully specified static route
default static route
12. Refer to the graphic. Which command would be used on router A to configure a static route to direct traffic from LAN A that is destined for LAN C?

A(config)# ip route 192.168.4.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.5.2
A(config)# ip route 192.168.4.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.3.2*
A(config)# ip route 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.3.2
A(config)# ip route 192.168.3.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.3.1
A(config)# ip route 192.168.3.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.4.0
13. Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator needs to configure a default route on the Border router. Which command would the administrator use to configure a default route that will require the least amount of router processing when forwarding packets?

Border(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 198.133.219.5
Border(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 198.133.219.6
Border(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/1*
Border(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/0
14. What two pieces of information are needed in a fully specified static route to eliminate recursive lookups? (Choose two.)
the interface ID exit interface*
the interface ID of the next-hop neighbor
the IP address of the next-hop neighbor*
the administrative distance for the destination network
the IP address of the exit interface
15. Refer to the exhibit. What command would be used to configure a static route on R1 so that traffic from both LANs can reach the 2001:db8:1:4::/64 remote network?

ipv6 route ::/0 serial0/0/0
ipv6 route 2001:db8:1:4::/64 2001:db8:1:3::1
ipv6 route 2001:db8:1:4::/64 2001:db8:1:3::2*
ipv6 route 2001:db8:1::/65 2001:db8:1:3::1
16. Refer to the exhibit. Which default static route command would allow R1 to potentially reach all unknown networks on the Internet?

R1(config)# ipv6 route 2001:db8:32::/64 G0/0
R1(config)# ipv6 route ::/0 G0/0 fe80::2
R1(config)# ipv6 route ::/0 G0/1 fe80::2*
R1(config)# ipv6 route 2001:db8:32::/64 G0/1 fe80::2
17. Consider the following command:
ip route 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.10.2 5
Which route would have to go down in order for this static route to appear in the routing table?
a default route
a static route to the 192.168.10.0/24 network*
an OSPF-learned route to the 192.168.10.0/24 network
an EIGRP-learned route to the 192.168.10.0/24 network
18. Refer to the exhibit. The routing table for R2 is as follows:

Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 2 subnets
C 10.0.0.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
C 10.0.0.4 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1
192.168.10.0/26 is subnetted, 3 subnets
S 192.168.10.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
C 192.168.10.64 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
S 192.168.10.128 [1/0] via 10.0.0.6
What will router R2 do with a packet destined for 192.168.10.129?
drop the packet
send the packet out interface Serial0/0/0
send the packet out interface Serial0/0/1*
send the packet out interface FastEthernet0/0
19. A network administrator has entered a static route to an Ethernet LAN that is connected to an adjacent router. However, the route is not shown in the routing table. Which command would the administrator use to verify that the exit interface is up?
show ip interface brief*
show ip protocols
show ip route
tracert
20. Consider the following command:
ip route 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.10.2 5
How would an administrator test this configuration?
Delete the default gateway route on the router.
Ping any valid address on the 192.168.10.0/24 network.
Manually shut down the router interface used as a primary route.*
Ping from the 192.168.10.0 network to the 10.10.10.2 addres
21. Refer to the exhibit. The small company shown uses static routing. Users on the R2 LAN have reported a problem with connectivity. What is the issue?

R2 needs a static route to the R1 LANs.
R1 and R2 must use a dynamic routing protocol.
R1 needs a default route to R2.
R1 needs a static route to the R2 LAN.*
R2 needs a static route to the Internet.
22. Which three IOS troubleshooting commands can help to isolate problems with a static route? (Choose three.)
show version
ping*
tracert
show ip route*
show ip interface brief*
show arp
23. An administrator issues the ipv6 route 2001:db8:acad:1::/32 gigabitethernet0/0 2001:db8:acad:6::1 100 command on a router. What administrative distance is assigned to this route?
0
1
32
100*
24. Refer to the exhibit. The network engineer for the company that is shown wants to use the primary ISP connection for all external connectivity. The backup ISP connection is used only if the primary ISP connection fails. Which set of commands would accomplish this goal?
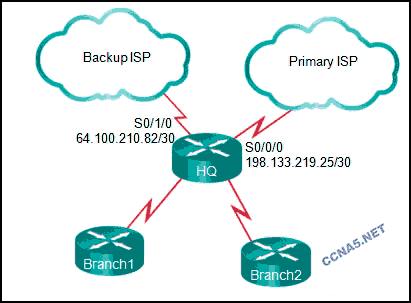
ip route 198.133.219.24 255.255.255.252
ip route 64.100.210.80 255.255.255.252
ip route 198.133.219.24 255.255.255.252
ip route 64.100.210.80 255.255.255.252 10
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/0
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/1/0
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/0
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/1/0 10*
25. Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
Why are the pings from PC0 to Server0 not successful?
The static route to network 192.168.1.0 is misconfigured on Router1.
The static route to network 192.168.1.0 is misconfigured on Router2.
The static route to network 192.168.2.0 is misconfigured on Router1.*
The static route to network 192.168.2.0 is misconfigured on Router2.
26. Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
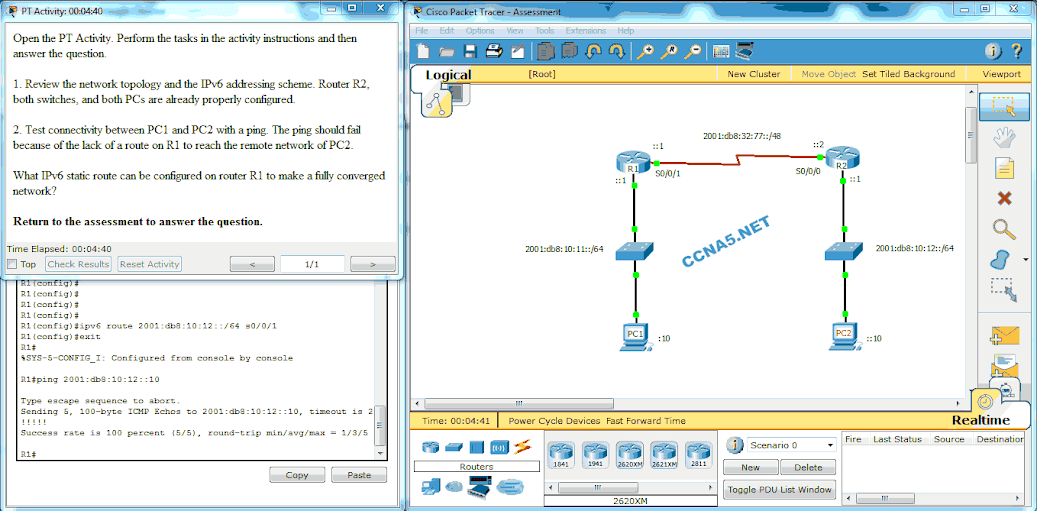
What IPv6 static route can be configured on router R1 to make a fully converged network?
ipv6 route 2001:db8:10:12::/64 S0/0/1*
ipv6 route 2001:db8:10:12::/64 S0/0/0
ipv6 route 2001:db8:10:12::/64 2001:db8:10:12::1
ipv6 route 2001:db8:10:12::/64 2001:db8:32:77::1
1. Which dynamic routing protocol was developed to interconnect different Internet service providers?
BGP*
EIGRP
OSPF
RIP
2. Which routing protocol is limited to smaller network implementations because it does not accommodate growth for larger networks?
OSPF
RIP*
EIGRP
IS-IS
3. What two tasks do dynamic routing protocols perform? (Choose two.)
discover hosts
update and maintain routing tables*
propagate host default gateways
network discovery*
assign IP addressing
4. When would it be more beneficial to use a dynamic routing protocol instead of static routing?
in an organization with a smaller network that is not expected to grow in size
on a stub network that has a single exit point
in an organization where routers suffer from performance issues
on a network where there is a lot of topology changes*
5. When would it be more beneficial to use static routing instead of dynamic routing protocols?
on a network where dynamic updates would pose a security risk*
on a network that is expected to continually grow in size
on a network that has a large amount of redundant paths
on a network that commonly experiences link failures
6. What is a purpose of the network command when configuring RIPv2 as the routing protocol?
It identifies the interfaces that belong to a specified network.*
It specifies the remote network that can now be reached.
It immediately advertises the specified network to neighbor routers with a classful mask.
It populates the routing table with the network entry.
7. A network administrator configures a static route on the edge router of a network to assign a gateway of last resort. How would a network administrator configure the edge router to automatically share this route within RIP?
Use the auto-summary command.
Use the passive-interface command.
Use the network command.
Use the default-information originate command.*
8. What is the purpose of the passive-interface command?
allows a routing protocol to forward updates out an interface that is missing its IP address
allows a router to send routing updates on an interface but not receive updates via that interface
allows an interface to remain up without receiving keepalives
allows interfaces to share IP addresses
allows a router to receive routing updates on an interface but not send updates via that interface*
9. Which route would be automatically created when a router interface is activated and configured with an IP address?
D 10.16.0.0/24 [90/3256] via 192.168.6.9
C 192.168.0.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet 0/0*
S 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet 0/1
O 172.16.0.0/16 [110/65] via 192.168.5.1
10. Refer to the exhibit. Which two types of routes could be used to describe the 192.168.200.0/30 route? (Choose two.)

ultimate route*
level 1 parent route
level 1 network route
level 2 child route*
supernet route
11. What occurs next in the router lookup process after a router identifies a destination IP address and locates a matching level 1 parent route?
The level 2 child routes are examined.*
The level 1 supernet routes are examined.
The level 1 ultimate routes are examined.
The router drops the packet.
12. Which route would be used to forward a packet with a source IP address of 192.168.10.1 and a destination IP address of 10.1.1.1?
C 192.168.10.0/30 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
S 10.1.0.0/16 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
O 10.1.1.0/24 [110/65] via 192.168.200.2, 00:01:20, Serial0/1/0*
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 172.16.1.1
13. Which two requirements are used to determine if a route can be considered as an ultimate route in a router’s routing table? (Choose two.)
contain subnets
be a default route
contain an exit interface*
be a classful network entry
contain a next-hop IP address*
14. What is a disadvantage of using dynamic routing protocols?
They are only suitable for simple topologies.
Their configuration complexity increases as the size of the network grows.
They send messages about network status insecurely across networks by default.*
They require administrator intervention when the pathway of traffic changes.
15. Which two statements are true regarding classless routing protocols? (Choose two.)
sends subnet mask information in routing updates*
sends complete routing table update to all neighbors
is supported by RIP version 1
allows for use of both 192.168.1.0/30 and 192.168.1.16/28 subnets in the same topology*
reduces the amount of address space available in an organization
16. Refer to the exhibit. Based on the partial output from the show ip route command, what two facts can be determined about the RIP routing protocol? (Choose two.)

RIP version 2 is running on this router and its RIP neighbor.*
The metric to the network 172.16.0.0 is 120.
RIP version 1 is running on this router and its RIP neighbor.
The command no auto-summary has been used on the RIP neighbor router.*
RIP will advertise two networks to its neighbor.
17. While configuring RIPv2 on an enterprise network, an engineer enters the command network 192.168.10.0 into router configuration mode.
What is the result of entering this command?
The interface of the 192.168.10.0 network is sending version 1 and version 2 updates.
The interface of the 192.168.10.0 network is receiving version 1 and version 2 updates.
The interface of the 192.168.10.0 network is sending only version 2 updates.*
The interface of the 192.168.10.0 network is sending RIP hello messages.
18. A destination route in the routing table is indicated with a code D. Which kind of route entry is this?
a static route
a route used as the default gateway
a network directly connected to a router interface
a route dynamically learned through the EIGRP routing protocol*
19. Refer to the exhibit. Which interface will be the exit interface to forward a data packet with the destination IP address 172.16.0.66?

Serial0/0/0
Serial0/0/1*
GigabitEthernet0/0
GigabitEthernet0/1
20. Which type of route will require a router to perform a recursive lookup?
an ultimate route that is using a next hop IP address on a router that is not using CEF*
a level 2 child route that is using an exit interface on a router that is not using CEF
a level 1 network route that is using a next hop IP address on a router that is using CEF
a parent route on a router that is using CEF
21. Which route is the best match for a packet entering a router with a destination address of 10.16.0.2?
S 10.0.0.0/8 [1/0] via 192.168.0.2
S 10.16.0.0/24 [1/0] via 192.168.0.9*
S 10.16.0.0/16 is directly connected, Ethernet 0/1
S 10.0.0.0/16 is directly connected, Ethernet 0/0
22. A router is configured to participate in multiple routing protocol: RIP, EIGRP, and OSPF. The router must send a packet to network 192.168.14.0. Which route will be used to forward the traffic?
a 192.168.14.0/26 route that is learned via RIP*
a 192.168.14.0/24 route that is learned via EIGRP
a 192.168.14.0/25 route that is learned via OSPF
a 192.168.14.0/25 route that is learned via RIP
23. What is different between IPv6 routing table entries compared to IPv4 routing table entries?
IPv6 routing tables include local route entries which IPv4 routing tables do not.
By design IPv6 is classless so all routes are effectively level 1 ultimate routes.*
The selection of IPv6 routes is based on the shortest matching prefix, unlike IPv4 route selection which is based on the longest matching prefix.
IPv6 does not use static routes to populate the routing table as used in IPv4.
24. Match the dynamic routing protocol component to the characteristic. (Not all options are used.)

data structures
tables or databases that are stored in RAM
routing protocol messages
exchanges routing information and maintains accurate information about networks
algorithm
a finite list of steps used to determine the best path
25. Match the characteristic to the corresponding type of routing. (Not all options are used.)

Place the options in the following order:
[+] typically used on stub networks
[+] less routing overhead
[#] new networks are added automatically to the routing table
[#] best choice for large networks
1. A network designer must provide a rationale to a customer for a design which will move an enterprise from a flat network topology to a hierarchical network topology. Which two features of the hierarchical design make it the better choice? (Choose two.)
lower bandwidth requirements
reduced cost for equipment and user training
easier to provide redundant links to ensure higher availability*
less required equipment to provide the same performance levels
simpler deployment for additional switch equipment*
2. What is a collapsed core in a network design?
a combination of the functionality of the access and distribution layers
a combination of the functionality of the distribution and core layers*
a combination of the functionality of the access and core layers
a combination of the functionality of the access, distribution, and core layers
3. What is a definition of a two-tier LAN network design?
access and core layers collapsed into one tier, and the distribution layer on a separate tier
access and distribution layers collapsed into one tier, and the core layer on a separate tier
distribution and core layers collapsed into one tier, and the access layer on a separate tier*
access, distribution, and core layers collapsed into one tier, with a separate backbone layer
4. What is a basic function of the Cisco Borderless Architecture distribution layer?
acting as a backbone
aggregating all the campus blocks
aggregating Layer 3 routing boundaries*
providing access to end user devices
5. Which two previously independent technologies should a network administrator attempt to combine after choosing to upgrade to a converged network infrastructure? (Choose two.)
user data traffic*
VoIP phone traffic*
scanners and printers
mobile cell phone traffic
electrical system
6. A local law firm is redesigning the company network so that all 20 employees can be connected to a LAN and to the Internet. The law firm would prefer a low cost and easy solution for the project. What type of switch should be selected?
fixed configuration*
modular configuration
stackable configuration
StackPower
StackWise
7. What are two advantages of modular switches over fixed-configuration switches? (Choose two.)
lower cost per switch
increased scalability*
lower forwarding rates
need for fewer power outlets*
availability of multiple ports for bandwidth aggregation
8. Which type of address does a switch use to build the MAC address table?
destination IP address
source IP address
destination MAC address
source MAC address*
9. Which network device can be used to eliminate collisions on an Ethernet network?
firewall
hub
router
switch*
10. What two criteria are used by a Cisco LAN switch to decide how to forward Ethernet frames? (Choose two.)
path cost
egress port
ingress port*
destination IP address
destination MAC address*
11. Refer to the exhibit. Consider that the main power has just been restored. PC3 issues a broadcast IPv4 DHCP request. To which port will SW1 forward this request?

to Fa0/1 only
to Fa0/1 and Fa0/2 only
to Fa0/1, Fa0/2, and Fa0/3 only*
to Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, and Fa0/4
to Fa0/1, Fa0/2, and Fa0/4 only
12. What is one function of a Layer 2 switch?
forwards data based on logical addressing
duplicates the electrical signal of each frame to every port
learns the port assigned to a host by examining the destination MAC address
determines which interface is used to forward a frame based on the destination MAC address*
13. Refer to the exhibit. How is a frame sent from PCA forwarded to PCC if the MAC address table on switch SW1 is empty?

SW1 floods the frame on all ports on the switch, excluding the interconnected port to switch SW2 and the port through which the frame entered the switch.
SW1 floods the frame on all ports on SW1, excluding the port through which the frame entered the switch.*
SW1 forwards the frame directly to SW2. SW2 floods the frame to all ports connected to SW2, excluding the port through which the frame entered the switch.
SW1 drops the frame because it does not know the destination MAC address.
14. A small publishing company has a network design such that when a broadcast is sent on the LAN, 200 devices receive the transmitted broadcast. How can the network administrator reduce the number of devices that receive broadcast traffic?
Add more switches so that fewer devices are on a particular switch.
Replace the switches with switches that have more ports per switch. This will allow more devices on a particular switch.
Segment the LAN into smaller LANs and route between them.*
Replace at least half of the switches with hubs to reduce the size of the broadcast domain.
15. Refer to the exhibit. How many broadcast domains are displayed?

1
4
8*
16
55
16. Which solution would help a college alleviate network congestion due to collisions?
a firewall that connects to two Internet providers
a high port density switch*
a router with two Ethernet ports
a router with three Ethernet ports
17. Which network device can serve as a boundary to divide a Layer 2 broadcast domain?
router*
Ethernet bridge
Ethernet hub
access point
18. What is the destination address in the header of a broadcast frame?
0.0.0.0
255.255.255.255
11-11-11-11-11-11
FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF*
19. Which statement describes a result after multiple Cisco LAN switches are interconnected?
The broadcast domain expands to all switches.*
One collision domain exists per switch.
Frame collisions increase on the segments connecting the switches.
There is one broadcast domain and one collision domain per switch.
20. What does the term “port density” represent for an Ethernet switch?
the memory space that is allocated to each switch port
the number of available ports*
the numbers of hosts that are connected to each switch port
the speed of each port
21. What are two reasons a network administrator would segment a network with a Layer 2 switch? (Choose two.)
to create fewer collision domains
to enhance user bandwidth*
to create more broadcast domains
to eliminate virtual circuits
to isolate traffic between segments*
to isolate ARP request messages from the rest of the network
22. Fill in the blank.
A converged network is one that uses the same infrastructure to carry voice, data, and video signals.
23. Match the borderless switched network guideline description to the principle. (Not all options are used.)

Place the options in the following order:
allows intelligent traffic load sharing by using all network resources -> flexibility
facilitates understanding the role of each device at every tier, simplifies deployment, operation, management, and reduces fault domains at every tier -> hierarchical
allows seamless network expansion and integrated service enablement on an on-demand basis -> modularity
satisfies user expectations for keeping the network always on -> resiliency
24. Match the functions to the corresponding layers. (Not all options are used.)

Place the options in the following order:
Access layer
[+] represents the network edge
[+] provides network access to the user
Distribution layer
[#] implements network access policy
[#] establishes Layer 3 routing boundaries
Core layer
[*] provides high-speed backbone connectivity
[*] functions as an aggregator for all the campus blocks
25. Match the forwarding characteristic to its type. (Not all options are used.)

Place the options in the following order:
cut-throught:
+appropriate for high perfomance computing applications
+forwarding process can be begin after receiving the destination address
+may forward invalid frames
store-and-forward:
#error checking before forwarding
#forwarding process only begins after receiving the entire frame
#only forwards valid frames
1. Which statement describes the port speed LED on the Cisco Catalyst 2960 switch?
If the LED is green, the port is operating at 100 Mb/s.*
If the LED is off, the port is not operating.
If the LED is blinking green, the port is operating at 10 Mb/s.
If the LED is amber, the port is operating at 1000 Mb/s.
2. Which command is used to set the BOOT environment variable that defines where to find the IOS image file on a switch?
config-register
boot system*
boot loader
confreg
3. What is a function of the switch boot loader?
to speed up the boot process
to provide security for the vulnerable state when the switch is booting
to control how much RAM is available to the switch during the boot process
to provide an environment to operate in when the switch operating system cannot be found*
4. Which interface is the default location that would contain the IP address used to manage a 24-port Ethernet switch?
VLAN 1*
Fa0/0
Fa0/1
interface connected to the default gateway
VLAN 99
5. A production switch is reloaded and finishes with a Switch> prompt. What two facts can be determined? (Choose two.)
POST occurred normally.*
The boot process was interrupted.
There is not enough RAM or flash on this router.
A full version of the Cisco IOS was located and loaded.*
The switch did not locate the Cisco IOS in flash, so it defaulted to ROM.
6. Which two statements are true about using full-duplex Fast Ethernet? (Choose two.)
Performance is improved with bidirectional data flow.*
Latency is reduced because the NIC processes frames faster.
Nodes operate in full-duplex with unidirectional data flow.
Performance is improved because the NIC is able to detect collisions.
Full-duplex Fast Ethernet offers 100 percent efficiency in both directions.*
7. In which situation would a technician use the show interfaces switch command?
to determine if remote access is enabled
when packets are being dropped from a particular directly attached host*
when an end device can reach local devices, but not remote devices
to determine the MAC address of a directly attached network device on a particular interface
8. Refer to the exhibit. A network technician is troubleshooting connectivity issues in an Ethernet network with the command show interfaces fastEthernet 0/0. What conclusion can be drawn based on the partial output in the exhibit?

All hosts on this network communicate in full-duplex mode.
Some workstations might use an incorrect cabling type to connect to the network.
There are collisions in the network that cause frames to occur that are less than 64 bytes in length.
A malfunctioning NIC can cause frames to be transmitted that are longer than the allowed maximum length.*
9. Refer to the exhibit. What media issue might exist on the link connected to Fa0/1 based on the show interface command?

The bandwidth parameter on the interface might be too high.
There could be an issue with a faulty NIC.
There could be too much electrical interference and noise on the link.*
The cable attaching the host to port Fa0/1 might be too long.
The interface might be configured as half-duplex.
10. If one end of an Ethernet connection is configured for full duplex and the other end of the connection is configured for half duplex, where would late collisions be observed?
on both ends of the connection
on the full-duplex end of the connection
only on serial interfaces
on the half-duplex end of the connection*
11. What is one difference between using Telnet or SSH to connect to a network device for management purposes?
Telnet uses UDP as the transport protocol whereas SSH uses TCP.
Telnet does not provide authentication whereas SSH provides authentication.
Telnet supports a host GUI whereas SSH only supports a host CLI.
Telnet sends a username and password in plain text, whereas SSH encrypts the username and password.*
12. Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator wants to configure Switch1 to allow SSH connections and prohibit Telnet connections. How should the network administrator change the displayed configuration to satisfy the requirement?

Use SSH version 1.
Reconfigure the RSA key.
Configure SSH on a different line.
Modify the transport input command.*
13. What is the effect of using the switchport port-security command?
enables port security on an interface*
enables port security globally on the switch
automatically shuts an interface down if applied to a trunk port
detects the first MAC address in a frame that comes into a port and places that MAC address in the MAC address table
14. Where are dynamically learned MAC addresses stored when sticky learning is enabled with the switchport port-security mac-address sticky command?
ROM
RAM*
NVRAM
flash
15. A network administrator configures the port security feature on a switch. The security policy specifies that each access port should allow up to two MAC addresses. When the maximum number of MAC addresses is reached, a frame with the unknown source MAC address is dropped and a notification is sent to the syslog server. Which security violation mode should be configured for each access port?
restrict*
protect
warning
shutdown
16. Which two statements are true regarding switch port security? (Choose two.)
The three configurable violation modes all log violations via SNMP.
Dynamically learned secure MAC addresses are lost when the switch reboots.*
The three configurable violation modes all require user intervention to re-enable ports.
After entering the sticky parameter, only MAC addresses subsequently learned are converted to secure MAC addresses.
If fewer than the maximum number of MAC addresses for a port are configured statically, dynamically learned addresses are added to CAM until the maximum number is reached.*
17. Which action will bring an error-disabled switch port back to an operational state?
Remove and reconfigure port security on the interface.
Issue the switchport mode access command on the interface.
Clear the MAC address table on the switch.
Issue the shutdown and then no shutdown interface commands.*
18. Refer to the exhibit. Port Fa0/2 has already been configured appropriately. The IP phone and PC work properly. Which switch configuration would be most appropriate for port Fa0/2 if the network administrator has the following goals?

No one is allowed to disconnect the IP phone or the PC and connect some other wired device.
If a different device is connected, port Fa0/2 is shut down.
The switch should automatically detect the MAC address of the IP phone and the PC and add those addresses to the running configuration.
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 2
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 2
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky*
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 2
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security violation restrict
19. Refer to the exhibit. What can be determined about port security from the information that is shown?

The port has been shut down.
The port has two attached devices.
The port violation mode is the default for any port that has port security enabled.*
The port has the maximum number of MAC addresses that is supported by a Layer 2 switch port which is configured for port security.
20. Refer to the exhibit. Which event will take place if there is a port security violation on switch S1 interface Fa0/1?

A notification is sent.
A syslog message is logged.
Packets with unknown source addresses will be dropped.*
The interface will go into error-disabled state.
21. Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.

Fill in the blank.
Do not use abbreviations.What is the missing command on S1? “ ip address 192.168.99.2 255.255.255.0 ”
22. Match the step to each switch boot sequence description. (Not all options are used.)

Place the options in the following order:
step 3
– not scored –
step 1
step 4
step 2
step 5
step 6
23. Identify the steps needed to configure a switch for SSH. The answer order does not matter. (Not all options are used.)

Place the options in the following order:
[+] Create a local user.
[+] Generate RSA keys.
[+] Configure a domain name.
[+] Use the login local command.
[+] Use the transport input ssh command.
[+] Order does not matter within this group.
24. Match the link state to the interface and protocol status. (Not all options are used.)

Place the options in the following order:
disable -> administratively down
Layer 1 problem -> down/down
– not scored –
Layer 2 problem -> up/down
operational -> up/up
1. What are three primary benefits of using VLANs? (Choose three.)
security*
a reduction in the number of trunk links
cost reduction*
end user satisfaction
improved IT staff efficiency*
no required configuration
2. Which type of VLAN is used to designate which traffic is untagged when crossing a trunk port?
data
default
native*
management
3. A network administrator is determining the best placement of VLAN trunk links. Which two types of point-to-point connections utilize VLAN trunking? (Choose two.)
between two switches that utilize multiple VLANs*
between a switch and a client PC
between a switch and a server that has an 802.1Q NIC*
between a switch and a network printer
between two switches that share a common VLAN
4. What must the network administrator do to remove Fast Ethernet port fa0/1 from VLAN 2 and assign it to VLAN 3?
Enter the no vlan 2 and the vlan 3 commands in global configuration mode.
Enter the switchport access vlan 3 command in interface configuration mode.*
Enter the switchport trunk native vlan 3 command in interface configuration mode.
Enter the no shutdown command in interface configuration mode to return it to the default configuration and then configure the port for VLAN 3.
5. When a Cisco switch receives untagged frames on a 802.1Q trunk port, which VLAN ID is the traffic switched to by default?
unused VLAN ID
native VLAN ID*
data VLAN ID
management VLAN ID
6. Port Fa0/11 on a switch is assigned to VLAN 30. If the command no switchport access vlan 30 is entered on the Fa0/11 interface, what will happen?
Port Fa0/11 will be shutdown.
An error message would be displayed.
Port Fa0/11 will be returned to VLAN 1.*
VLAN 30 will be deleted.
7. Which command is used to remove only VLAN 20 from a switch?
delete vlan.dat
delete flash:vlan.dat
no vlan 20*
no switchport access vlan 20
8. What happens to a port that is associated with VLAN 10 when the administrator deletes VLAN 10 from the switch?
The port becomes inactive.*
The port goes back to the default VLAN.
The port automatically associates itself with the native VLAN.
The port creates the VLAN again.
9. Which two characteristics match extended range VLANs? (Choose two.)
CDP can be used to learn and store these VLANs.
VLAN IDs exist between 1006 to 4094.
They are saved in the running-config file by default.*
VLANs are initialized from flash memory.
They are commonly used in small networks.
10. A Cisco switch currently allows traffic tagged with VLANs 10 and 20 across trunk port Fa0/5. What is the effect of issuing a switchport trunk allowed vlan 30 command on Fa0/5?
It allows VLANs 1 to 30 on Fa0/5.
It allows VLANs 10, 20, and 30 on Fa0/5.
It allows only VLAN 30 on Fa0/5.*
It allows a native VLAN of 30 to be implemented on Fa0/5.
11. Refer to the exhibit. PC-A and PC-B are both in VLAN 60. PC-A is unable to communicate with PC-B. What is the problem?

The native VLAN should be VLAN 60.
The native VLAN is being pruned from the link.
The trunk has been configured with the switchport nonegotiate command.
The VLAN that is used by PC-A is not in the list of allowed VLANs on the trunk.*
12. Refer to the exhibit. DLS1 is connected to another switch, DLS2, via a trunk link. A host that is connected to DLS1 is not able to communicate to a host that is connected to DLS2, even though they are both in VLAN 99. Which command should be added to Fa0/1 on DLS1 to correct the problem?

switchport nonegotiate
switchport mode dynamic auto
switchport trunk native vlan 66*
switchport trunk allowed vlan add 99
13. What is a characteristic of legacy inter-VLAN routing?
Only one VLAN can be used in the topology.
The router requires one Ethernet link for each VLAN.*
The user VLAN must be the same ID number as the management VLAN.
Inter-VLAN routing must be performed on a switch instead of a router.
14. What is a disadvantage of using router-on-a-stick inter-VLAN routing?
does not support VLAN-tagged packets
requires the use of more physical interfaces than legacy inter-VLAN routing
does not scale well beyond 50 VLANs*
requires the use of multiple router interfaces configured to operate as access links
15. Refer to the exhibit. Router RA receives a packet with a source address of 192.168.1.35 and a destination address of 192.168.1.85. What will the router do with this packet?

The router will drop the packet.
The router will forward the packet out interface FastEthernet 0/1.1.
The router will forward the packet out interface FastEthernet 0/1.2.*
The router will forward the packet out interface FastEthernet 0/1.3.
The router will forward the packet out interface FastEthernet 0/1.2 and interface FastEthernet 0/1.3.
16. Refer to the exhibit. In what switch mode should port G0/1 be assigned if Cisco best practices are being used?

access
trunk*
native
auto
17. A small college uses VLAN 10 for the classroom network and VLAN 20 for the office network. What is needed to enable communication between these two VLANs while using legacy inter-VLAN routing?
A router with at least two LAN interfaces should be used.*
Two groups of switches are needed, each with ports that are configured for one VLAN.
A router with one VLAN interface is needed to connect to the SVI on a switch.
A switch with a port that is configured as trunk is needed to connect to a router.
18. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator needs to configure router-on-a-stick for the networks that are shown. How many subinterfaces will have to be created on the router if each VLAN that is shown is to be routed and each VLAN has its own subinterface?

1
2
3
4*
5
19. When configuring a router as part of a router-on-a-stick inter-VLAN routing topology, where should the IP address be assigned?
to the interface
to the subinterface*
to the SVI
to the VLAN
20. A high school uses VLAN15 for the laboratory network and VLAN30 for the faculty network. What is required to enable communication between these two VLANs while using the router-on-a-stick approach?
A multilayer switch is needed.
A router with at least two LAN interfaces is needed.
Two groups of switches are needed, each with ports that are configured for one VLAN.
A switch with a port that is configured as a trunk is needed when connecting to the router.*
21. Refer to the exhibit. A router-on-a-stick configuration was implemented for VLANs 15, 30, and 45, according to the show running-config command output. PCs on VLAN 45 that are using the 172.16.45.0 /24 network are having trouble connecting to PCs on VLAN 30 in the 172.16.30.0 /24 network. Which error is most likely causing this problem?

The wrong VLAN has been configured on GigabitEthernet 0/0.45.
The command no shutdown is missing on GigabitEthernet 0/0.30.
The GigabitEthernet 0/0 interface is missing an IP address.
There is an incorrect IP address configured on GigabitEthernet 0/0.30.*
22. Match the IEEE 802.1Q standard VLAN tag field with the descriptions. (Not all options are used.)

Place the options in the following order:
User Priority –> value that supports level or service implementation
Type –> value for the tag protocol ID value
Canonical Format Identifier –> identifier that enables Token Ring frames to be carried across Ethernet Links
– not scored – -value for the application protocol of the user data in a frame
VLAN ID –> VLAN number
23. Fill in the blank. Use the full command syntax.
The show vlan command displays the VLAN assignment for all ports as well as the existing VLANs on the switch.
24. Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
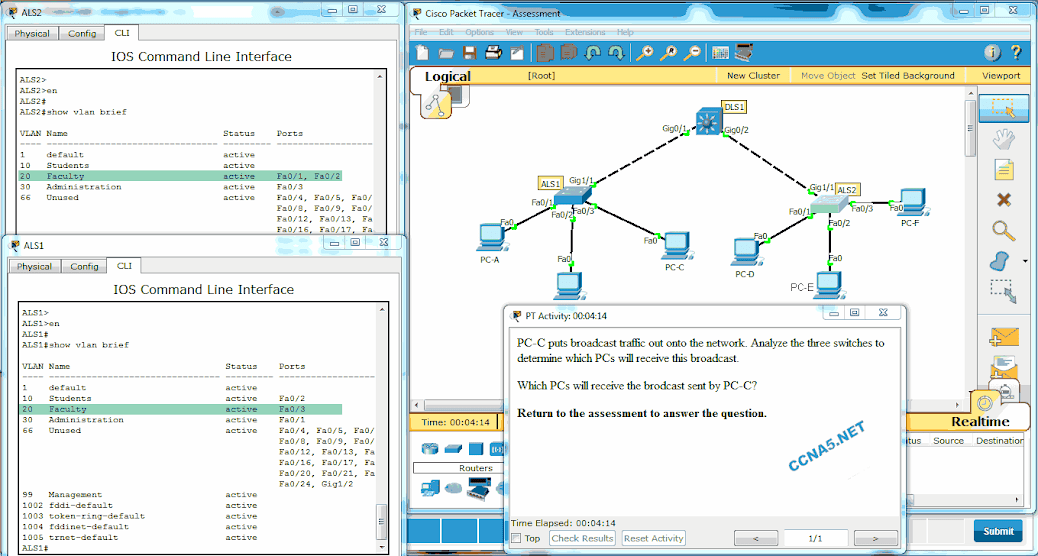
Which PCs will receive the broadcast sent by PC-C?
PC-A, PC-B
PC-D, PC-E*
PC-A, PC-B, PC-E
PC-A, PC-B, PC-D, PC-E
PC-A, PC-B, PC-D, PC-E, PC-F
1. In which configuration would an outbound ACL placement be preferred over an inbound ACL placement?
when the ACL is applied to an outbound interface to filter packets coming from multiple inbound interfaces before the packets exit the interface*
when a router has more than one ACL
when an outbound ACL is closer to the source of the traffic flow
when an interface is filtered by an outbound ACL and the network attached to the interface is the source network being filtered within the ACL
2. Which address is required in the command syntax of a standard ACL?
source MAC address
destination MAC address
source IP address*
destination IP address
3. Which statement describes a difference between the operation of inbound and outbound ACLs?
In contrast to outbound ALCs, inbound ACLs can be used to filter packets with multiple criteria.
Inbound ACLs can be used in both routers and switches but outbound ACLs can be used only on routers.
Inbound ACLs are processed before the packets are routed while outbound ACLs are processed after the routing is completed.*
On a network interface, more than one inbound ACL can be configured but only one outbound ACL can be configured.
4. Which three statements describe ACL processing of packets? (Choose three.)
An implicit deny any rejects any packet that does not match any ACE.*
A packet can either be rejected or forwarded as directed by the ACE that is matched.*
A packet that has been denied by one ACE can be permitted by a subsequent ACE.
A packet that does not match the conditions of any ACE will be forwarded by default.
Each statement is checked only until a match is detected or until the end of the ACE list.*
Each packet is compared to the conditions of every ACE in the ACL before a forwarding decision is made.
5. What single access list statement matches all of the following networks?
192.168.16.0
192.168.17.0
192.168.18.0
192.168.19.0
access-list 10 permit 192.168.16.0 0.0.3.255*
access-list 10 permit 192.168.16.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 10 permit 192.168.16.0 0.0.15.255
access-list 10 permit 192.168.0.0 0.0.15.255
6. A network administrator needs to configure a standard ACL so that only the workstation of the administrator with the IP address 192.168.15.23 can access the virtual terminal of the main router. Which two configuration commands can achieve the task? (Choose two.)
Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit host 192.168.15.23*
Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit 192.168.15.23 0.0.0.0*
Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit 192.168.15.23 0.0.0.255
Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit 192.168.15.23 255.255.255.0
Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit 192.168.15.23 255.255.255.255
7. If a router has two interfaces and is routing both IPv4 and IPv6 traffic, how many ACLs could be created and applied to it?
4
6
8*
12
16
8. Which three statements are generally considered to be best practices in the placement of ACLs? (Choose three.)
Place standard ACLs close to the source IP address of the traffic.
Place extended ACLs close to the destination IP address of the traffic.
Filter unwanted traffic before it travels onto a low-bandwidth link.*
Place extended ACLs close to the source IP address of the traffic.*
Place standard ACLs close to the destination IP address of the traffic.*
For every inbound ACL placed on an interface, there should be a matching outbound ACL.
9. Refer to the exhibit. Which command would be used in a standard ACL to allow only devices on the network attached to R2 G0/0 interface to access the networks attached to R1?
access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.63
access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.96 0.0.0.31*
access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.128 0.0.0.63
10. Refer to the exhibit. If the network administrator created a standard ACL that allows only devices that connect to the R2 G0/0 network access to the devices on the R1 G0/1 interface, how should the ACL be applied?
inbound on the R2 G0/0 interface
outbound on the R1 G0/1 interface*
inbound on the R1 G0/1 interface
outbound on the R2 S0/0/1 interface
11. Refer to the following output. What is the significance of the 4 match(es) statement?
R1# <output omitted>
10 permit 192.168.1.56 0.0.0.7
20 permit 192.168.1.64 0.0.0.63 (4 match(es))
30 deny any (8 match(es))
Four packets have been denied that have been sourced from any IP address.
Four packets have been denied that are destined for the 192.168.1.64 network.
Four packets have been allowed through the router from PCs in the network of 192.168.1.64.*
Four packets have been allowed through the router to reach the destination network of 192.168.1.64/26.
12. On which router should the show access-lists command be executed?
on the router that routes the packet referenced in the ACL to the final destination network
on the router that routes the packet referenced in the ACL from the source network
on any router through which the packet referenced in the ACL travels
on the router that has the ACL configured*
13. What is the quickest way to remove a single ACE from a named ACL?
Use the no keyword and the sequence number of the ACE to be removed.*
Use the no access-list command to remove the entire ACL, then recreate it without the ACE.
Copy the ACL into a text editor, remove the ACE, then copy the ACL back into the router.
Create a new ACL with a different number and apply the new ACL to the router interface.
14. Which feature will require the use of a named standard ACL rather than a numbered standard ACL?
the ability to filter traffic based on a specific protocol
the ability to filter traffic based on an entire protocol suite and destination
the ability to specify source and destination addresses to use when identifying traffic
the ability to add additional ACEs in the middle of the ACL without deleting and re-creating the list*
15. An administrator has configured an access list on R1 to allow SSH administrative access from host 172.16.1.100. Which command correctly applies the ACL?
R1(config-if)# ip access-group 1 in
R1(config-if)# ip access-group 1 out
R1(config-line)# access-class 1 in*
R1(config-line)# access-class 1 out
16. Which type of router connection can be secured by the access-class command?
vty*
console
serial
Ethernet
17. Consider the following output for an ACL that has been applied to a router via the access-class in command. What can a network administrator determine from the output that is shown?
R1# <output omitted>
Standard IP access list 2
10 permit 192.168.10.0, wildcard bits 0.0.0.255 (2 matches)
20 deny any (1 match)
Two devices connected to the router have IP addresses of 192.168.10.x.
Traffic from one device was not allowed to come into one router port and be routed outbound a different router port.
Two devices were able to use SSH or Telnet to gain access to the router.*
Traffic from two devices was allowed to enter one router port and be routed outbound to a different router port.
18. Refer to the exhibit. A router has an existing ACL that permits all traffic from the 172.16.0.0 network. The administrator attempts to add a new ACE to the ACL that denies packets from host 172.16.0.1 and receives the error message that is shown in the exhibit. What action can the administrator take to block packets from host 172.16.0.1 while still permitting all other traffic from the 172.16.0.0 network?

Manually add the new deny ACE with a sequence number of 5.*
Manually add the new deny ACE with a sequence number of 15.
Create a second access list denying the host and apply it to the same interface.
Add a deny any any ACE to access-list 1.
19. Refer to the exhibit. An ACL was configured on R1 with the intention of denying traffic from subnet 172.16.4.0/24 into subnet 172.16.3.0/24. All other traffic into subnet 172.16.3.0/24 should be permitted. This standard ACL was then applied outbound on interface Fa0/0. Which conclusion can be drawn from this configuration?
Only traffic from the 172.16.4.0/24 subnet is blocked, and all other traffic is allowed.
An extended ACL must be used in this situation.
The ACL should be applied to the FastEthernet 0/0 interface of R1 inbound to accomplish the requirements.
All traffic will be blocked, not just traffic from the 172.16.4.0/24 subnet.*
The ACL should be applied outbound on all interfaces of R1.
20. Refer to the exhibit. What will happen to the access list 10 ACEs if the router is rebooted before any other commands are implemented?

The ACEs of access list 10 will be deleted.
The ACEs of access list 10 will not be affected.
The ACEs of access list 10 will be renumbered.*
The ACEs of access list 10 wildcard masks will be converted to subnet masks.
21. What is the effect of configuring an ACL with only ACEs that deny traffic?
The ACL will permit any traffic that is not specifically denied.
The ACL will block all traffic.*
The ACL must be applied inbound only.
The ACL must be applied outbound only.
22. Which type of ACL statements are commonly reordered by the Cisco IOS as the first ACEs?
host*
range
permit any
lowest sequence number
23. A network administrator is configuring an ACL to restrict access to certain servers in the data center. The intent is to apply the ACL to the interface connected to the data center LAN. What happens if the ACL is incorrectly applied to an interface in the inbound direction instead of the outbound direction?
All traffic is denied.
All traffic is permitted.
The ACL does not perform as designed.*
The ACL will analyze traffic after it is routed to the outbound interface.
24. When would a network administrator use the clear access-list counters command?
when obtaining a baseline
when buffer memory is low
when an ACE is deleted from an ACL
when troubleshooting an ACL and needing to know how many packets matched*
25. Match each statement with the example subnet and wildcard that it describes. (Not all options are used.)

Place the options in the following order:
192.168.15.65 255.255.255.240 ==> the first valid host address in a subnet
192.168.15.144 0.0.0.15 ==> subnetwork address of a subnet with 14 valid host addreses
host 192.168.15.2 ==> all IP address bits must match exactly
192.168.5.0 0.0.3.255 ==> hosts in a subnet with SM 255.255.252.0
192.168.3.64 0.0.0.7 ==> address with a subnet 255.255.255.248
1. Which DHCPv4 message will a client send to accept an IPv4 address that is offered by a DHCP server?
unicast DHCPACK
broadcast DHCPACK
unicast DHCPREQUEST
broadcast DHCPREQUEST*
2. A company uses DHCP servers to dynamically assign IPv4 addresses to employee workstations. The address lease duration is set as 5 days. An employee returns to the office after an absence of one week. When the employee boots the workstation, it sends a message to obtain an IP address. Which Layer 2 and Layer 3 destination addresses will the message contain?
FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF and 255.255.255.255*
both MAC and IPv4 addresses of the DHCP server
MAC address of the DHCP server and 255.255.255.255
FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF and IPv4 address of the DHCP server
3. Which is a DHCPv4 address allocation method that assigns IPv4 addresses for a limited lease period?
manual allocation
pre-allocation
automatic allocation
dynamic allocation*
4. Which address does a DHCPv4 server target when sending a DHCPOFFER message to a client that makes an address request?
client IP address
client hardware address*
gateway IP address
broadcast MAC address
5. As a DHCPv4 client lease is about to expire, what is the message that the client sends the DHCP server?
DHCPDISCOVER
DHCPOFFER
DHCPREQUEST*
DHCPACK
6. What is an advantage of configuring a Cisco router as a relay agent?
It will allow DHCPDISCOVER messages to pass without alteration.
It can forward both broadcast and multicast messages on behalf of clients.
It can provide relay services for multiple UDP services.*
It reduces the response time from a DHCP server.
7. An administrator issues the commands:
Router(config)# interface g0/1
Router(config-if)# ip address dhcp
What is the administrator trying to achieve?
configuring the router to act as a DHCPv4 server
configuring the router to obtain IP parameters from a DHCPv4 server*
configuring the router to act as a relay agent
configuring the router to resolve IP address conflicts
8. Under which two circumstances would a router usually be configured as a DHCPv4 client? (Choose two.)
The router is intended to be used as a SOHO gateway.*
The administrator needs the router to act as a relay agent.
The router is meant to provide IP addresses to the hosts.
This is an ISP requirement.*
The router has a fixed IP address.
9. A company uses the SLAAC method to configure IPv6 addresses for the employee workstations. Which address will a client use as its default gateway?
the all-routers multicast address
the link-local address of the router interface that is attached to the network*
the unique local address of the router interface that is attached to the network
the global unicast address of the router interface that is attached to the network
10. A network administrator configures a router to send RA messages with M flag as 0 and O flag as 1. Which statement describes the effect of this configuration when a PC tries to configure its IPv6 address?
It should contact a DHCPv6 server for all the information that it needs.
It should use the information that is contained in the RA message exclusively.
It should use the information that is contained in the RA message and contact a DHCPv6 server for additional information.*
It should contact a DHCPv6 server for the prefix, the prefix-length information, and an interface ID that is both random and unique.
11. A company implements the stateless DHCPv6 method for configuring IPv6 addresses on employee workstations. After a workstation receives messages from multiple DHCPv6 servers to indicate their availability for DHCPv6 service, which message does it send to a server for configuration information?
DHCPv6 SOLICIT
DHCPv6 REQUEST
DHCPv6 ADVERTISE
DHCPv6 INFORMATION-REQUEST*
12. An administrator wants to configure hosts to automatically assign IPv6 addresses to themselves by the use of Router Advertisement messages, but also to obtain the DNS server address from a DHCPv6 server. Which address assignment method should be configured?
SLAAC
stateless DHCPv6*
stateful DHCPv6
RA and EUI-64
13. How does an IPv6 client ensure that it has a unique address after it configures its IPv6 address using the SLAAC allocation method?
It sends an ARP message with the IPv6 address as the destination IPv6 address.
It checks with the IPv6 address database that is hosted by the SLAAC server.
It contacts the DHCPv6 server via a special formed ICMPv6 message.
It sends an ICMPv6 Neighbor Solicitation message with the IPv6 address as the target IPv6 address.*
14. What is used in the EUI-64 process to create an IPv6 interface ID on an IPv6 enabled interface?
the MAC address of the IPv6 enabled interface*
a randomly generated 64-bit hexadecimal address
an IPv6 address that is provided by a DHCPv6 server
an IPv4 address that is configured on the interface
15. What two methods can be used to generate an interface ID by an IPv6 host that is using SLAAC? (Choose two.)
EUI-64*
random generation*
stateful DHCPv6
DAD
ARP
16. Refer to the exhibit. Based on the output that is shown, what kind of IPv6 addressing is being configured?

CCNA v6.0 chapter 8 Q16
SLAAC
stateful DHCPv6
stateless DHCPv6*
static link-local
17. Refer to the exhibit. What should be done to allow PC-A to receive an IPv6 address from the DHCPv6 server?

CCNA v6.0 chapter 8 Q17
Add the ipv6 dhcp relay command to interface Fa0/0.*
Configure the ipv6 nd managed-config-flag command on interface Fa0/1.
Change the ipv6 nd managed-config-flag command to ipv6 nd other-config-flag.
Add the IPv6 address 2001:DB8:1234:5678::10/64 to the interface configuration of the DHCPv6 server.
18. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is implementing stateful DHCPv6 operation for the company. However, the clients are not using the prefix and prefix-length information that is configured in the DHCP pool. The administrator issues a show ipv6 interface command. What could be the cause of the problem?

CCNA v6.0 chapter 8 Q18
No virtual link-local address is configured.
The Duplicate Address Detection feature is disabled.
The router is configured for SLAAC DHCPv6 operation.
The router is configured for stateless DHCPv6 operation*
19. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is implementing the stateless DHCPv6 operation for the company. Clients are configuring IPv6 addresses as expected. However, the clients are not getting the DNS server address and the domain name information configured in the DHCP pool. What could be the cause of the problem?

CCNA v6.0 chapter 8 Q19
The GigabitEthernet interface is not activated.
The router is configured for SLAAC operation.*
The DNS server address is not on the same network as the clients are on.
The clients cannot communicate with the DHCPv6 server, evidenced by the number of active clients being 0.
20. Fill in the blank. Do not abbreviate.
Type a command to exclude the first fifteen useable IP addresses from a DHCPv4 address pool of the network 10.0.15.0/24.
Router(config)# ip dhcp excluded-address 10.0.15.1 10.0.15.15
21. Order the steps of configuring a router as a DHCPv4 server. (Not all options are used.)

CCNA v6.0 chapter 8 Q21
Place the options in the following order:
[+] Step 2 -> Configure a DHCP pool.
[+] Step 1 -> Exclude IP addresses.
– not scored –
[+] Step 3 ->Define the default gateway router
– not scored –
22. Match the descriptions to the corresponding DHCPv6 sever type. (Not all options are used.)
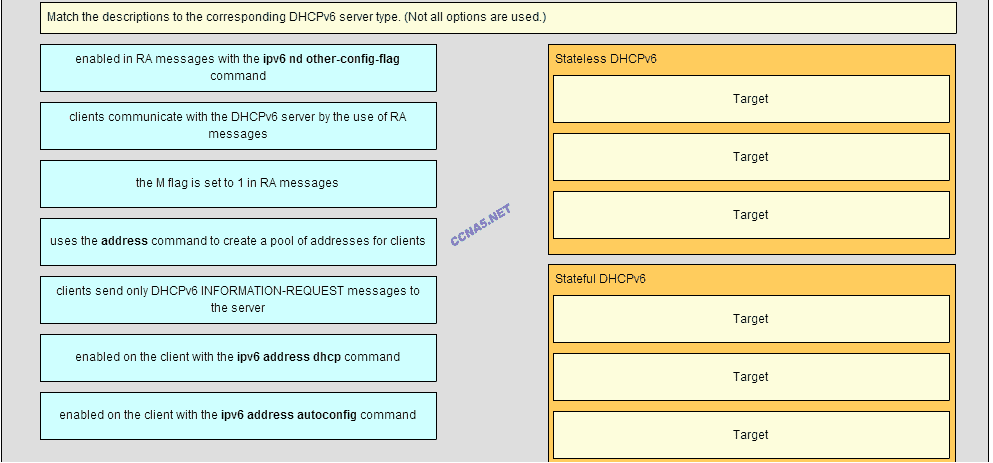
CCNA v6.0 chapter 8 Q22
Place the options in the following order:
Stateless DHCPv6
[+] enabled in RA messages with the ipv6 nd other-config-flag command
[+] clients send only DHCPv6 INFORMATION-REQUEST messages to the server
[+] enabled on the client with the ipv6 address autoconfig command
Stateful DHCPv6
[#] the M flag is set to 1 in RA messages
[#] uses the address command to create a pool of addresses for clients
[#] enabled on the client with the ipv6 address dhcp command
1. Which method is used by a PAT-enabled router to send incoming packets to the correct inside hosts?
It uses the destination TCP or UDP port number on the incoming packet.*
It uses the source IP address on the incoming packet.
It uses the source TCP or UDP port number on the incoming packet.
It uses a combination of the source TCP or UDP port number and the destination IP address on the incoming packet.
2. Refer to the exhibit. Which address or addresses represent the inside global address?

10.1.1.2
any address in the 10.1.1.0 network
192.168.0.100
209.165.20.25*
3 Fill in the blank. Do not use abbreviations.
NAT overload is also known as “Port Address Translation”
4. A network administrator is configuring a static NAT on the border router for a web server located in the DMZ network. The web server is configured to listen on TCP port 8080. The web server is paired with the internal IP address of 192.168.5.25 and the external IP address of 209.165.200.230. For easy access by hosts on the Internet, external users do not need to specify the port when visiting the web server. Which command will configure the static NAT?
R1(config)# ip nat inside source static tcp 192.168.5.25 80 209.165.200.230 8080
R1(config)# ip nat inside source static tcp 192.168.5.25 8080 209.165.200.230 80*
R1(config)# ip nat inside source static tcp 209.165.200.230 80 192.168.5.25 8080
R1(config)# ip nat inside source static tcp 209.165.200.230 8080 192.168.5.25 80
5. What is defined by the ip nat pool command when configuring dynamic NAT?
the pool of available NAT servers
the range of external IP addresses that internal hosts are permitted to access
the range of internal IP addresses that are translated
the pool of global address*
6. Refer to the exhibit. Based on the output that is shown, what type of NAT has been implemented?

dynamic NAT with a pool of two public IP addresses
PAT using an external interface*
static NAT with one entry
static NAT with a NAT pool
7. What is the primary purpose of NAT?
conserve IPv4 addresses*
increase network security
allow peer-to-peer file sharing
enhance network performance
8. What is the major benefit of using NAT with Port Address Translation?
It allows external hosts access to internal servers.
It improves network performance for real-time protocols.
It allows many internal hosts to share the same public IPv4 address.*
It provides a pool of public addresses that can be assigned to internal hosts.
9. What is a characteristic of unique local addresses?
They allow sites to be combined without creating any address conflicts.*
They are designed to improve the security of IPv6 networks.
Their implementation depends on ISPs providing the service.
They are defined in RFC 3927.
10. A network administrator configures the border router with the command R1(config)# ip nat inside source list 4 pool corp. What is required to be configured in order for this particular command to be functional?
a NAT pool named corp that defines the starting and ending public IP addresses*
an access list named corp that defines the private addresses that are affected by NAT
an access list numbered 4 that defines the starting and ending public IP addresses
ip nat outside to be enabled on the interface that connects to the LAN affected by the NAT
a VLAN named corp to be enabled and active and routed by R1
11. Which statement describes IPv6 ULAs?
They conserve IPv6 address space.
They begin with the fe80::/10 prefix.
They are assigned by an ISP.
They are not routable across the internet.*
12. What is the purpose of port forwarding?
Port forwarding allows an external user to reach a service on a private IPv4 address that is located inside a LAN.*
Port forwarding allows users to reach servers on the Internet that are not using standard port numbers.
Port forwarding allows an internal user to reach a service on a public IPv4 address that is located outside a LAN.
Port forwarding allows for translating inside local IP addresses to outside local addresses.
13. When dynamic NAT without overloading is being used, what happens if seven users attempt to access a public server on the Internet when only six addresses are available in the NAT pool?
No users can access the server.
The request to the server for the seventh user fails.*
All users can access the server.
The first user gets disconnected when the seventh user makes the request.
14. A network engineer has configured a router with the command ip nat inside source list 4 pool corp overload. Why did the engineer use the overload option?
The company has more private IP addresses than available public IP addresses.*
The company needs to have more public IP addresses available to be used on the Internet.
The company router must throttle or buffer traffic because the processing power of the router is not enough to handle the normal load of external-bound Internet traffic.
The company has a small number of servers that should be accessible by clients from the Internet.
15. Match the steps with the actions that are involved when an internal host with IP address 192.168.10.10 attempts to send a packet to and external server at the IP address 209.165.200.254 across a router R1 that running dynamic NAT. (Not all options are used.)

Place the options in the following order:
– not scored –
step 5 => R1 replaces the address 192.168.10.10 with a translated inside global address.
step 2 => R1 checks the NAT configuration to determine if this packet should be translated.
step 4 => R1 selects an available global address from the dynamic address pool.
step 1 => The cost sends packets that request a connection to the server at the address 209.165.200.254
step 3 => If there is no translation entry for this IP address, R1 determines that the source address 192.168.10.10 must be translated.
16. What is a disadvantage of NAT?
There is no end-to-end addressing.*
The router does not need to alter the checksum of the IPv4 packets.
The internal hosts have to use a single public IPv4 address for external communication.
The costs of readdressing hosts can be significant for a publicly addressed network.
17. Refer to the exhibit. What is the purpose of the command marked with an arrow shown in the partial configuration output of a Cisco broadband router?

defines which addresses can be translated*
defines which addresses are allowed into the router
defines which addresses are assigned to a NAT pool
defines which addresses are allowed out of the router
18. What are two of the required steps to configure PAT? (Choose two.)
Define a pool of global addresses to be used for overload translation.*
Create a standard access list to define applications that should be translated.
Define the range of source ports to be used.
Identify the inside interface.*
Define the hello and interval timers to match the adjacent neighbor router.
19. Refer to the exhibit. A technician is configuring R2 for static NAT to allow the client to access the web server. What is a possible reason that the client PC cannot access the web server?

Interface S0/0/0 should be identified as the outside NAT interface. *
Interface Fa0/1 should be identified as the outside NAT interface.
The IP NAT statement is incorrect.
The configuration is missing a valid access control list.
20. What are two benefits of NAT? (Choose two.)
It saves public IP addresses.*
It adds a degree of privacy and security to a network. *
It increases routing performance. It makes troubleshooting routing issues easier.
It makes tunneling with IPsec less complicated.
It makes troubleshooting routing issues easier.
21. What is an advantage of deploying IPv4 NAT technology for internal hosts in an organization?
makes internal network access easy for outside hosts using UDP
provides flexibility in designing the IPv4 addressing scheme*
increases the performance of packet transmission to the Internet
enables the easy deployment of applications that require end-to-end traceability
1. A ping fails when performed from router R1 to directly connected router R2. The network administrator then proceeds to issue the show cdp neighbors command. Why would the network administrator issue this command if the ping failed between the two routers?
The network administrator suspects a virus because the ping command did not work.
The network administrator wants to verify Layer 2 connectivity.*
The network administrator wants to verify the IP address configured on router R2.
The network administrator wants to determine if connectivity can be established from a non-directly connected network.
2. Which statement is true about CDP on a Cisco device?
The show cdp neighbor detail command will reveal the IP address of a neighbor only if there is Layer 3 connectivity.
To disable CDP globally, the no cdp enable command in interface configuration mode must be used.
CDP can be disabled globally or on a specific interface.*
Because it runs at the data link layer, the CDP protocol can only be implemented in switches.
3. Why would a network administrator issue the show cdp neigbors command on a router?
to display device ID and other information about directly connected Cisco devices*
to display router ID and other information about OSPF neighbors
to display line status and other information about directly connected Cisco devices
to display routing table and other information about directly connected Cisco devices
4. Refer to the exhibit. Routers R1 and R2 are connected via a serial link. One router is configured as the NTP master, and the other is an NTP client. Which two pieces of information can be obtained from the partial output of the show ntp associations detail command on R2? (Choose two.)
Both routers are configured to use NTPv2.
Router R1 is the master, and R2 is the client.*
Router R2 is the master, and R1 is the client.
The IP address of R1 is 192.168.1.2.*
The IP address of R2 is 192.168.1.2.
5. Which two statements are true about NTP servers in an enterprise network? (Choose two.)
There can only be one NTP server on an enterprise network.
All NTP servers synchronize directly to a stratum 1 time source.
NTP servers at stratum 1 are directly connected to an authoritative time source.*
NTP servers ensure an accurate time stamp on logging and debugging information.*
NTP servers control the mean time between failures (MTBF) for key network devices.
6. The command ntp server 10.1.1.1 is issued on a router. What impact does this command have?
determines which server to send system log files to
identifies the server on which to store backup configurations
ensures that all logging will have a time stamp associated with it
synchronizes the system clock with the time source with IP address 10.1.1.1*
7. Refer to the exhibit. Which two conclusions can be drawn from the syslog message that was generated by the router? (Choose two.)
This message resulted from an unusual error requiring reconfiguration of the interface.
This message indicates that the interface should be replaced.
This message is a level 5 notification message.*
This message indicates that service timestamps have been configured.*
This message indicates that the interface changed state five times.
8. Which protocol or service allows network administrators to receive system messages that are provided by network devices?
syslog*
NTP
SNMP
NetFlow
9. Which syslog message type is accessible only to an administrator and only via the Cisco CLI?
errors
debugging*
emergency
alerts
10. Refer to the exhibit. From what location have the syslog messages been retrieved?
syslog server
syslog client
router RAM*
router NVRAM
11. Refer to the exhibit. What does the number 17:46:26.143 represent?
the time passed since the syslog server has been started
the time when the syslog message was issued*
the time passed since the interfaces have been up
the time on the router when the show logging command was issued
12. What is used as the default event logging destination for Cisco routers and switches?
terminal line
syslog server
console line*
workstation
13. A network administrator has issued the logging trap 4 global configuration mode command. What is the result of this command?
After four events, the syslog client will send an event message to the syslog server.
The syslog client will send to the syslog server any event message that has a severity level of 4 and higher.
The syslog client will send to the syslog server any event message that has a severity level of 4 and lower.*
The syslog client will send to the syslog server event messages with an identification trap level of only 4.
14. What is the major release number in the IOS image name c1900-universalk9-mz.SPA.152-3.T.bin?
2
3
15*
52
1900
15. What statement describes a Cisco IOS image with the &##8220;universalk9_npe” designation for Cisco ISR G2 routers?
It is an IOS version that can only be used in the United States of America.
It is an IOS version that provides only the IPBase feature set.
It is an IOS version that offers all of the Cisco IOS Software feature sets.
It is an IOS version that, at the request of some countries, removes any strong cryptographic functionality.*
16. What code in the Cisco IOS 15 image filename c1900-universalk9-mz.SPA.153-3.M.bin indicates that the file is digitally signed by Cisco?
SPA*
universalk9
M
mz
17. Which two conditions should the network administrator verify before attempting to upgrade a Cisco IOS image using a TFTP server? (Choose two.)
Verify the name of the TFTP server using the show hosts command.
Verify that the TFTP server is running using the tftpdnld command.
Verify that the checksum for the image is valid using the show version command.
Verify connectivity between the router and TFTP server using the ping command.*
Verify that there is enough flash memory for the new Cisco IOS image using the show flash command.*
18. A network administrator configures a router with the command sequence:
R1(config)# boot system tftp://c1900-universalk9-mz.SPA.152-4.M3.bin
R1(config)# boot system rom
What is the effect of the command sequence?
On next reboot, the router will load the IOS image from ROM.
The router will copy the IOS image from the TFTP server and then reboot the system.
The router will load IOS from the TFTP server. If the image fails to load, it will load the IOS image from ROM.*
The router will search and load a valid IOS image in the sequence of flash, TFTP, and ROM.
19. A network engineer is upgrading the Cisco IOS image on a 2900 series ISR. What command could the engineer use to verify the total amount of flash memory as well as how much flash memory is currently available?
show flash0:*
show version
show interfaces
show startup-config
20. Beginning with the Cisco IOS Software Release 15.0, which license is a prerequisite for installing additional technology pack licenses?
IPBase*
DATA
UC
SEC
21. Which three software packages are available for Cisco IOS Release 15.0?
DATA*
IPVoice
Security*
Enterprise Services
Unified Communications*
Advanced IP Services
22. When a customer purchases a Cisco IOS 15.0 software package, what serves as the receipt for that customer and is used to obtain the license as well?
Software Claim Certificate
End User License Agreement
Unique Device Identifier
Product Activation Key*
23. In addition to IPBase, what are the three technology packs that are shipped within the universal Cisco IOS Software Release 15 image? (Choose three.)
Advanced IP Services
Advanced Enterprise Services
DATA*
Security*
SP Services
Unified Communications*
24. Which command would a network engineer use to find the unique device identifier of a Cisco router?
show version
show license udi*
show running-configuration
license install stored-location-url
25. Which command is used to configure a one-time acceptance of the EULA for all Cisco IOS software packages and features?
license save
show license
license boot module module-name
license accept end user agreement*
26. Refer to the exhibit. Match the components of the IOS image name to their description. (Not all options are used.)


